 Last night, protons collided in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at the record-breaking energy of 13 teraelectronvolts (TeV) for the first time. These test collisions were to set up systems that protect the machine and detectors from particles that stray from the edges of the beam. A key part of the process was the set-up of the collimators. These devices which absorb stray particles were adjusted in colliding-beam conditions. This set-up will give the accelerator team the data they need to ensure that the LHC magnets and detectors are fully protected. Today the tests continue. Colliding beams will stay in the LHC for several hours. The LHC Operations team will continue to monitor beam quality and optimisation of the set-up. This is an important part of the process that will allow the experimental teams running the detectors ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, LHCb, LHCf, MOEDAL and TOTEM to switch on their experiments fully. Data taking and the start of the LHC’s second run is planned for early June. source: www.cern.ch
Last night, protons collided in the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at the record-breaking energy of 13 teraelectronvolts (TeV) for the first time. These test collisions were to set up systems that protect the machine and detectors from particles that stray from the edges of the beam. A key part of the process was the set-up of the collimators. These devices which absorb stray particles were adjusted in colliding-beam conditions. This set-up will give the accelerator team the data they need to ensure that the LHC magnets and detectors are fully protected. Today the tests continue. Colliding beams will stay in the LHC for several hours. The LHC Operations team will continue to monitor beam quality and optimisation of the set-up. This is an important part of the process that will allow the experimental teams running the detectors ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, LHCb, LHCf, MOEDAL and TOTEM to switch on their experiments fully. Data taking and the start of the LHC’s second run is planned for early June. source: www.cern.ch
You might also be interested in

The record neutrino observed by KM3NeT
07 February 2025
Read more The record neutrino observed by KM3NeT

INFN celebrates the STEM WEEK and the International Day of Women and Girl in Science 2025

International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, 2025
03 February 2025
Read more International Year of Quantum Science and Technology, 2025

A new generation of plastic scintillators thanks to 3d printing
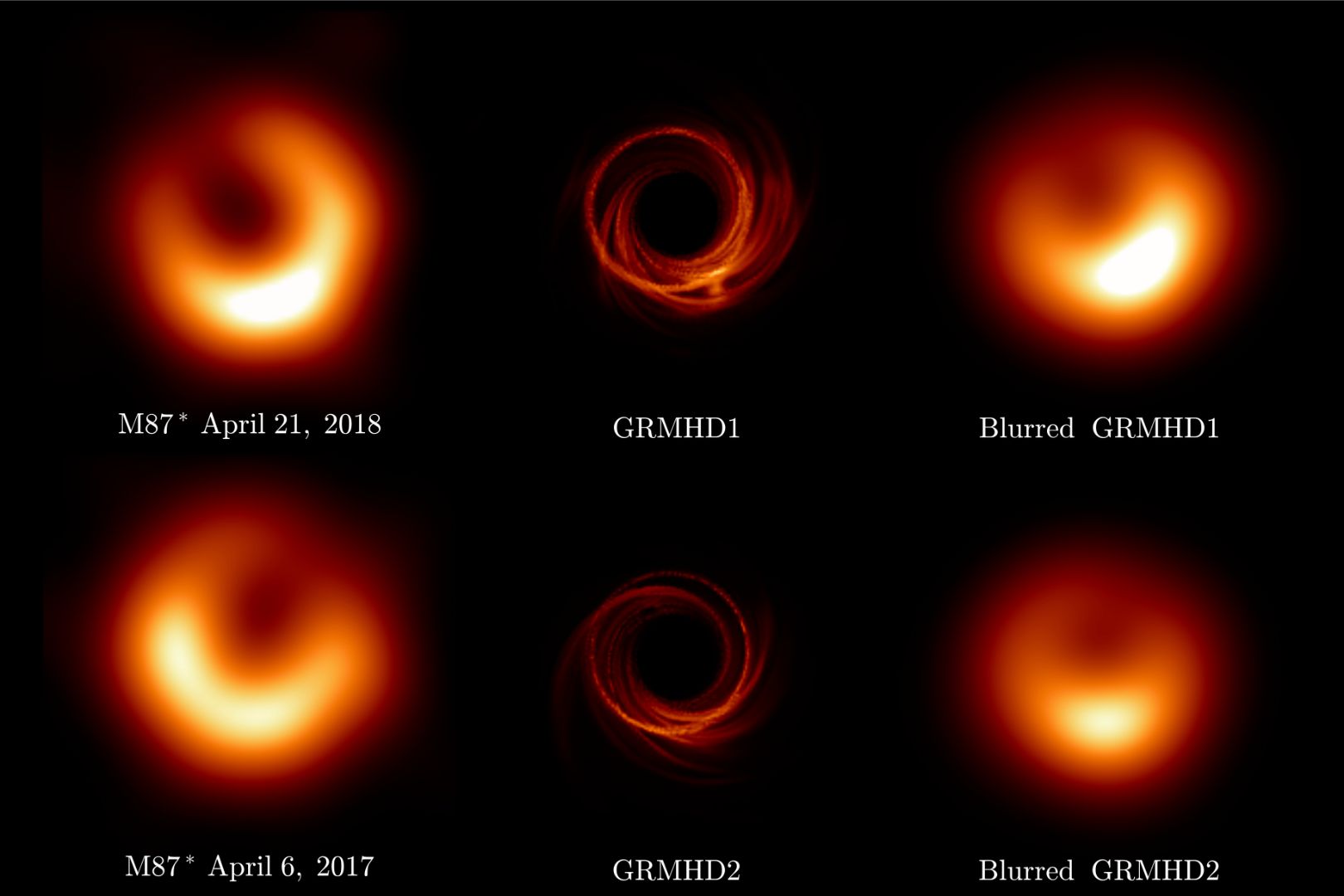
Capturing the accretion flow of M87* black hole
22 January 2025
Read more Capturing the accretion flow of M87* black hole
